SPECIAL ISSUE ON LOCUSTS
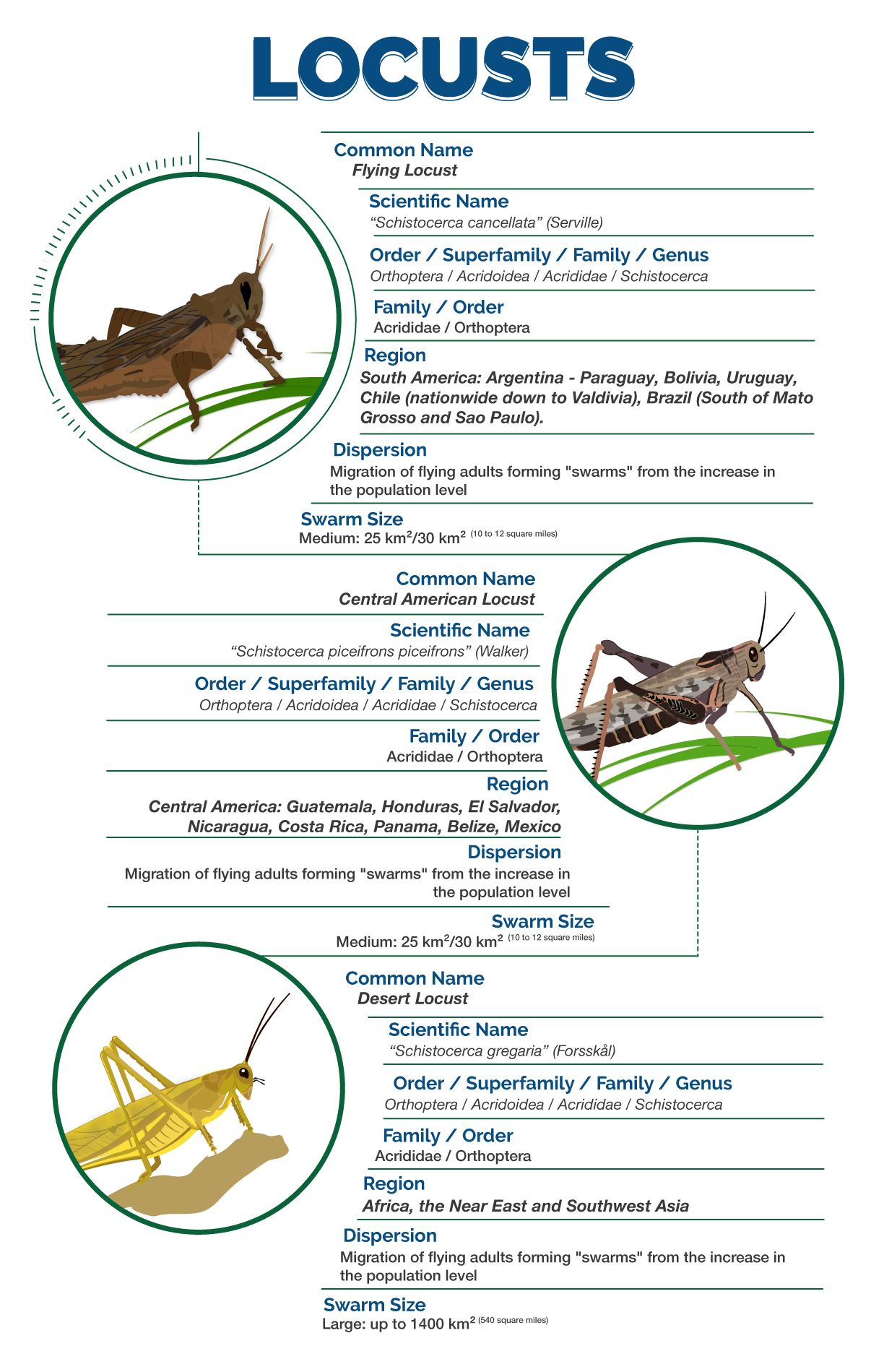
Are the locusts that affect Africa, Asia and Latin America the same?
In these three continents, the "locust" is present, represented by individuals of the same genus "Schistocerca” with different species, that is, in South America appears Schistocerca cancellata, Serville (1834) "Flying Locust”, in Central America Schistocerca piceifrons piceifrons, Walker (1870) “Central American Locust” and in Africa, Asia and the Middle East is found Schistocerca gregaria, Forsskål (1775) “Desert Locust”.
Presented by: Ing Agr Jorgelina Lezaun
Agribusiness & Marketing Consultant South America Region
jorgelina.lezaun@gmail.com
July 2020
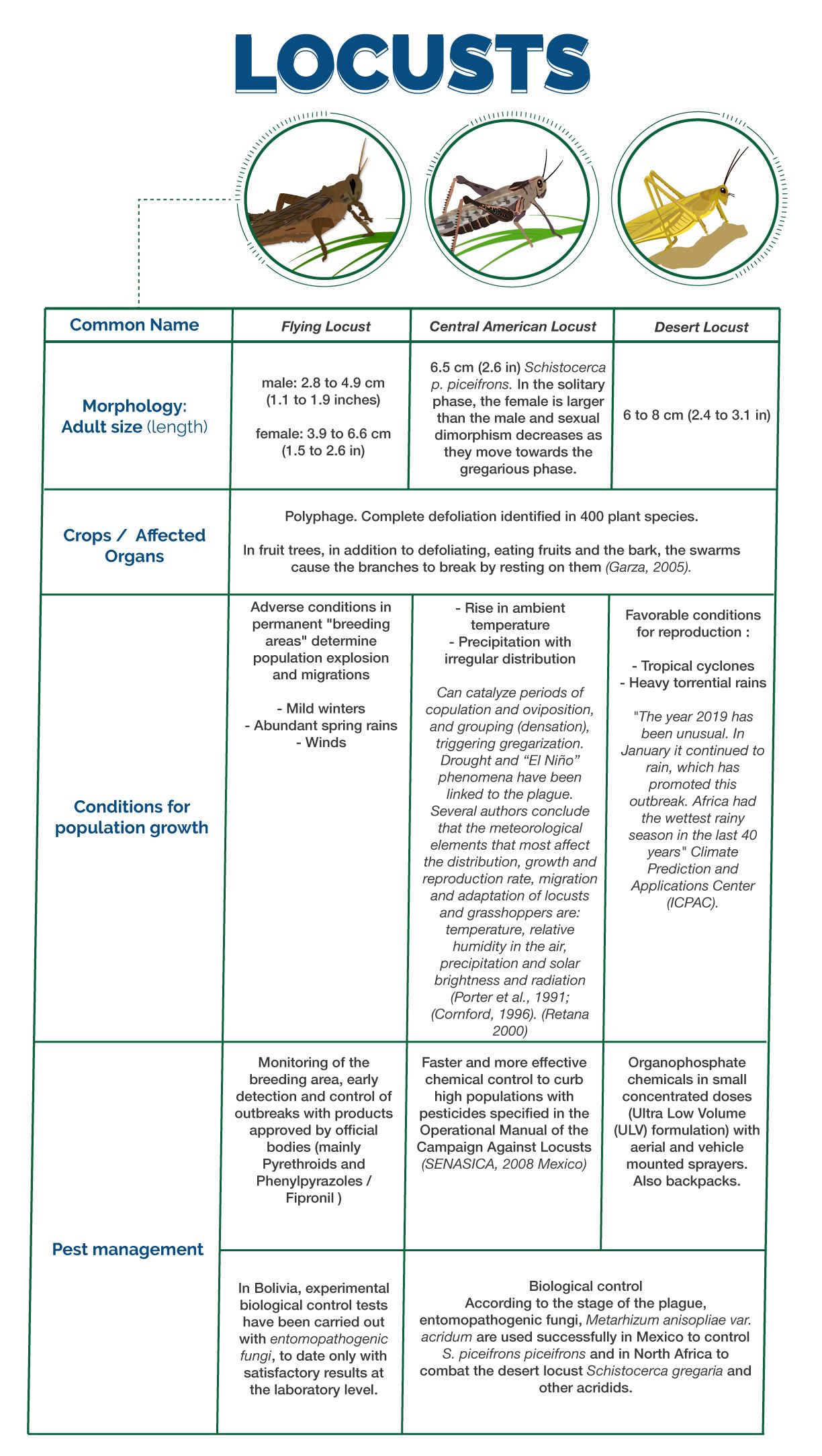
The locust is a cyclical, polyphagous and migratory pest with devastating effects. These insects present some interspecific differences but their life cycle, population habits and behavior are similar.
In all cases, they are highly specialized individuals that develop solitarily in desert environments. They live in low density and when environmental conditions are favorable there is a demographic explosion of populations in their permanent breeding areas and a change in behavior appears that takes them from the solitary phase to the gregarious phase in which they migrate forming "swarms”.
This change in habits is explained by the "Theory of Phases" developed by Boris Petrovich Uvarov (1889-1970), and it is a characteristic of locusts - which differentiates them from grasshoppers - their ability to change their behavior and physiology (color, size and shape) in response to changes in population density, from solitary to gregarious and vice versa.
The Desert Lobster stands out for its great voracity, also for being a species with adaptation to geographical areas with extreme environmental conditions. In addition, the location of its "permanent breeding sites" in places of difficult access and great extension determine the complexity to carry out phytosanitary surveillance.
This situation affects the possibility of early monitoring and control of the pest and has as a consequence a serious socioeconomic impact in countries of high vulnerability. For this reason, it is very important the support of international organizations, FAO and the global community in their fight to combat it and thus, contribute to the food and nutritional security of the population of these regions.
Why have outbreaks appeared simultaneously in recent years?
It is a cyclical plague and the climatic conditions have been particular in the three continents. The factors involved with the recent locust outbreaks are:
- Precipitation that provides the soil with the necessary moisture for the eggs and the growth of the vegetation that provides them with their food.
- Temperature should be ideal for egg hatching and development of nymphs. Greater high temperatures shorten the cycle.
- Wind that favors the migration of the swarms (Symmons y Cressman 2001), which causes these Acridian formations to move towards other countries or regions, making essential the regional coordination and intra-regional information exchange.
In recent years in South America there have been exceptional conditions with temperatures and rainfall above the average - mild winters with higher than average rainfall, which allowed this species to develop a third “additional” generation during the winter.
According to OIRSA experts, in Central America, there have been "favorable climatic conditions" given the storms caused by tropical storms Amanda and Cristobal between May and June 2020.
In Africa - especially in Ethiopia, Kenya and Somalia - according to FAO, the drought, high temperatures and floods in addition to a cyclone in early December 2019 increased the proliferation and presence of locusts in migration to areas with vegetation and plantations. This means that the region is facing the worst desert locust outbreak it has experienced in decades.