Find out where farmers take empty pesticide containers for an environmentally responsible solution.
July 2023
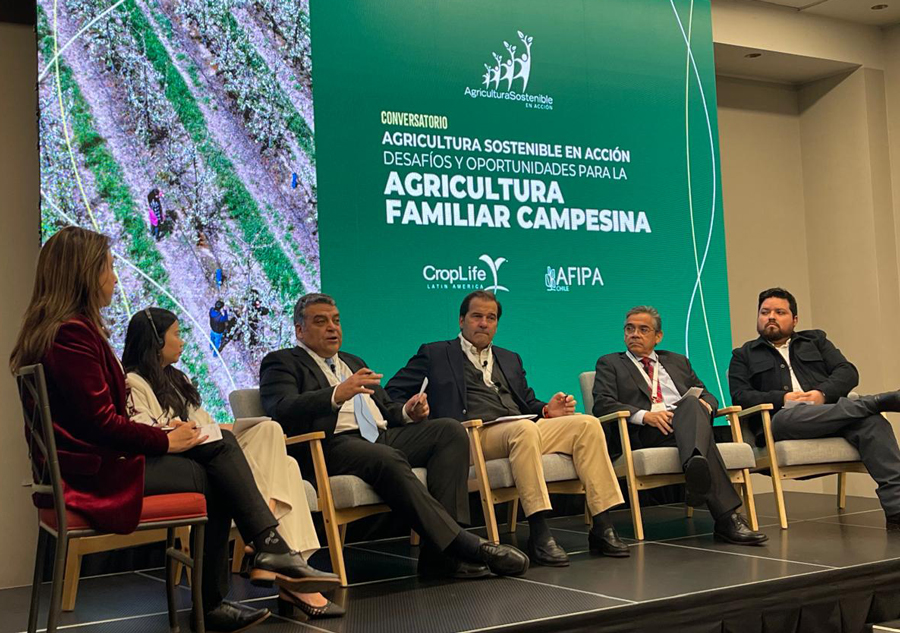
Facilitating the location of collection centers for receiving empty pesticide containers in the region allows us to see on a single map the impact of the CampoLimpioSM program that seeks to provide an environmentally responsible solution to these containers, says José Perdomo, President of CropLife Latin America.
CampoLimpioSM is a stewardship program for empty pesticide containers that contributes to the fulfillment of several Sustainable Development Goals by promoting production, responsible consumption and the development of the circular economy.
In the last 25 years, with the actions of CampoLimpioSM more than 700,000 tons of plastic have been recovered and processed from Latin American fields. A high percentage of this plastic has been recycled and turned into new products such as plastic wood; another part has been used for energy recovery in kilns.
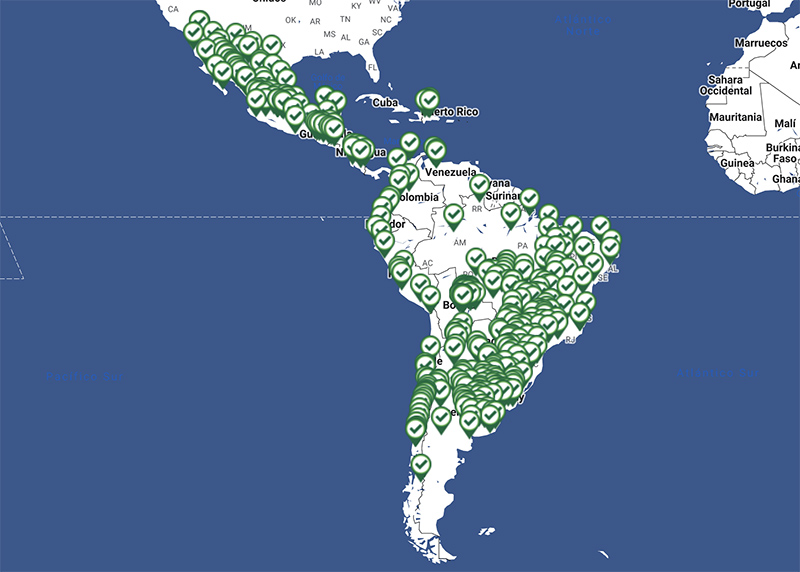
In this map that we are presenting today with more than 400 georeferenced collection centers, you can appreciate the logistics management required by CampoLimpioSM, highlights Gabriela Briceño, Program Director at CropLife Latin America. Each center demands planning that begins by defining its location in strategic places in such a way that they facilitate the delivery of the containers by the farmers. It must also be ensured that the design and construction comply with the adequate technical specifications for ventilation, size, safety and equipment.
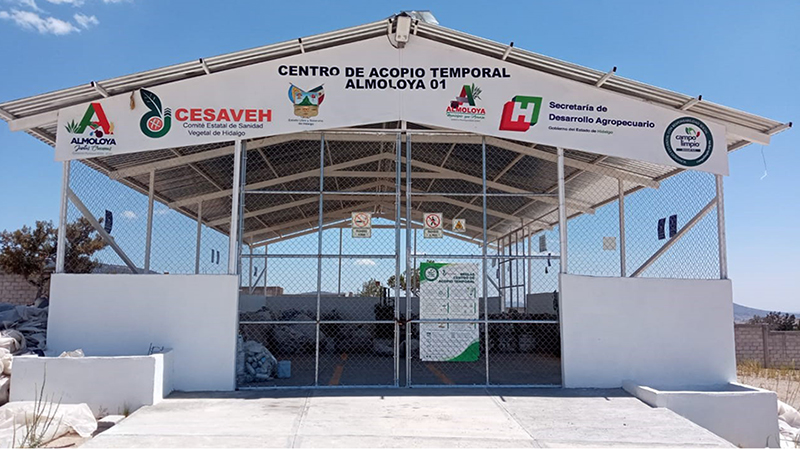
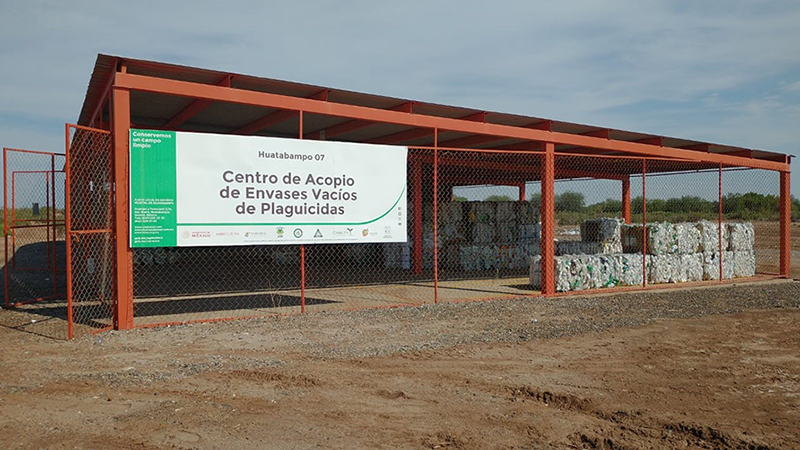


In order to maintain the proper operation of each collection center, the National Associations carry out logistics coordination work in which the reception and exit of containers is harmonized; they ensure that the receiving capacity is correct for the type of agriculture in the area. For these reasons, in the georeferencing that we did, we find not only the exact location and how to get there using Waze or Google Maps, but also the opening hours, the contact information of those responsible and the type of plastic that is received in each of the collection centers of the region, adds Gabriela Briceño.
The key for the program to offer a solution for removing the plastic from the fields and give it an adequate treatment is the participation of the entire agricultural chain, which includes farmers, dealers, manufacturers, recyclers, authorities and the civil society. In countries where mandatory laws have been issued for each link in the chain to participate and take responsibility for their part, the program works more effectively and efficiently, which is why we encourage associations to work with their governments to create these comprehensive laws for the chain, highlights José Perdomo.
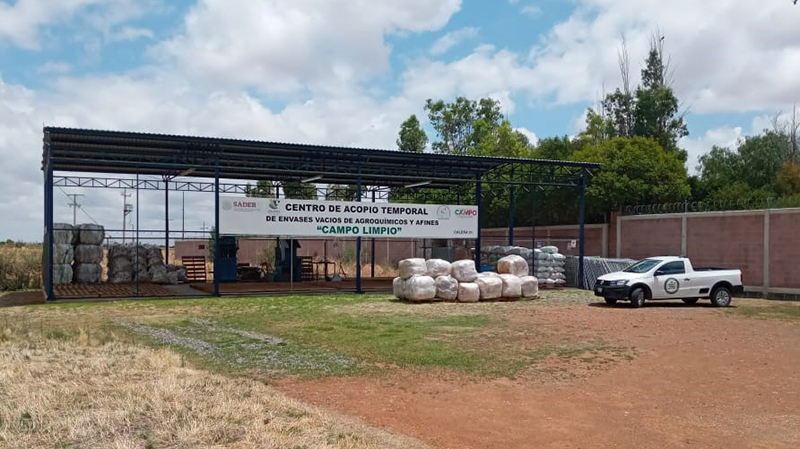
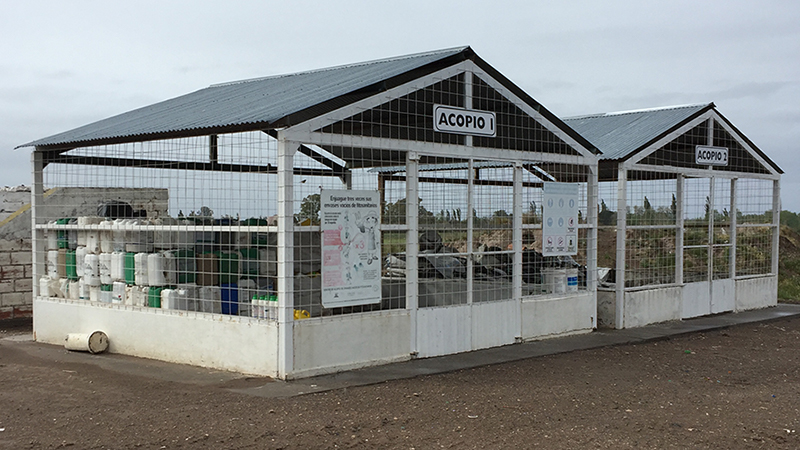


Roles and responsibilities of the agricultural chain
- It is essential that the agricultural producer triple wash or pressure wash the container, render it useless and take it to the nearest collection center. This works for the small, medium and large-scale farmer.
- The responsibility of the Collection Centers is also usually shared; in some countries the municipalities allocate a physical space for their construction and the distributors together with the manufacturers build it. Its administration is generally under the responsibility of the manufacturers through the national associations where they are affiliated. In some cases, there are other operators who are responsible for managing the collection centers.
- When the collection center has enough plastic, it must be transferred to its final destination. Some collection centers have machinery such as compactors or extruders that make it easier to transport a greater amount of plastic. This responsibility is in the hands of operators, distributors or manufacturers; it depends on the operation model of each country.
- The plastic is transferred to a recycling company that must comply with the entire environmental regulatory framework and where it can be turned into new products. Manufacturers authorize 80 possible uses for new products.
- The plastic that is taken to the kiln is usually a plastic that the farmer did not wash properly and therefore cannot be recycled, for this reason it is essential that farmers commit to triple washing or pressure washing. The kilns to which the plastic is taken are cement factories that comply with the regulations to use that plastic as energy recovery.
- Currently, in the recycling industry, new possibilities are being explored, such as chemical recycling, in which processes such as pyrolysis decompose the plastic, turning it into a new fuel.
The CampoLimpioSM program is an ally of the farmers; it is an environmental solution to the plastic that is taken to the field; it has allowed them to meet the demands of consumers regarding the environmental management that is expected of agricultural production. Latin America is a region that exports food. Every time a product is exported to other markets, farmers must certify that the plastic used in its production was properly treated. This is the solution that the CampoLimpioSM empty pesticide container management program offers and for which it is necessary to have the commitment of the entire chain and the authorities.